Printing Terminology: What is Die Cutting?
estimated reading time: 4 minutes
Understanding the use of Die Cutting in printing
In the printing industry, Die Cutting refers to a process
that uses sharpened steel blades to cut specific shapes, patterns, and designs in
paper, cardstock, or other materials.
The thin steel blades, known as rules, can be formed into a
variety of interesting shapes to add creativity and uniqueness to printed
pieces. The blades are engineered to produce clean and accurate cuts, ensuring
that each custom shape is consistent in size and quality.

Die-Cutting is like an industrial cookie cutter
The die cutting procedure functions very similar to a cookie cutter…where a preformed shape with a sharp perimeter edge is forced through a substrate using pressure.
In addition to adding a custom-shaped perimeter to
printed pieces, die cutting can also be used to cut shaped holes or "windows" within the printed pieces.
The Die Cutting Process
Once all the details and dimensions of the desired shape have
been determined, specialized software is used to create a layout of the shape.
After this layout has been finalized and approved, it is transferred to a base
material.
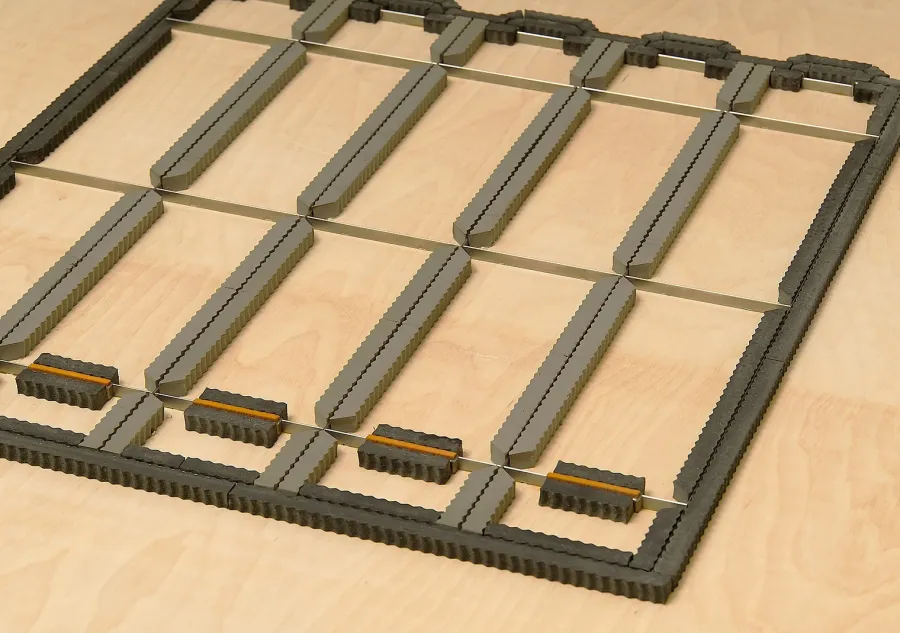
The most common base material is a strong and stable wood,
such as birch or maple. Nylon and composite boards are sometimes used as well. The outline
of the design is engraved into the base material using a laser or router. The cutting
process follows the design precisely to ensure the accuracy of the final
product.
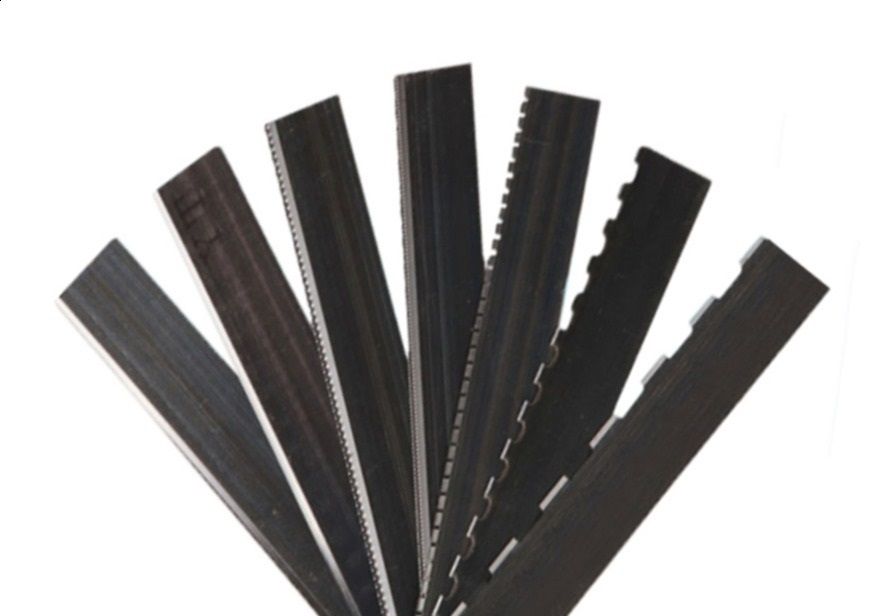
Steel rules, which have been sharpened to provide the cutting
edge, are fabricated to fit into the engraved grooves on the base. Usually made
from spring steel or stainless steel, the rules are carefully inserted into the
base. The insertion process is usually done by hand, using a wooden or rubber mallet to firmly secure the steel rules into the base.
For efficiency, the steel rule die making process often
creates multiple-up dies. This allows the die to cut a gang of shapes all at once. Not only does this practice save processing time, most multiple-up configurations nest the shapes tightly
together to minimize the amount of excess paper that will end up as scrap.
Also, in addition to the sharp rules used for cutting, other
types of steel rules can be used to add score lines or perforations to printed
pieces.
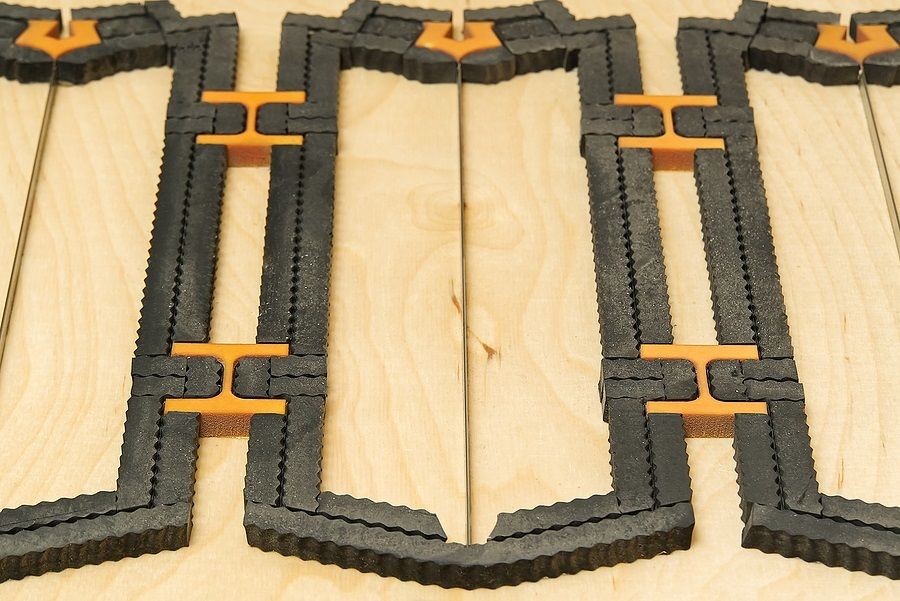

Once all the steel rules have been installed in the base,
pieces of sponge rubber are affixed to the base on both sides of the rules. These
spongy pieces are known as "ejection rubber." In addition to stabilizing the
substrate as the blades penetrate it, the ejection rubber acts to push the printed
substrate away from the die blades once it has been cut through. This makes for
easier removal of the finished pieces.
When the construction of the die unit is complete, it will be mounted into a machine that presses it into the printed substrate, creating a clean and precise cut. The die cutting machine is continually fed with printed sheets, cutting them quickly and accurately until the project is complete.

The Significance of Die Cutting in Printing
Die cutting serves several purposes in the printing
industry. First of all, it allows for the creation of custom shapes and designs
that cannot be achieved through traditional straight-line cutting methods. Because
customization makes a printed piece more visually interesting, it is particularly
effective for marketing materials where the goal is to create a memorable
impression.
Secondly, die cutting serves many functional purposes. A die cutting operation can be used to make custom index tabs, create hooks or holes for door hangers or tags, add business card slits to brochures or presentation folders, fabricate fold-out elements or rounded corners, and a host of other features essential to the functionality of many printed products.
Let Color Vision help you make a lasting impression...
In today's competitive business world, companies are always
looking for ways to stand out from the competition and make a positive,
long-lasting impression. Die Cutting can take a printed design to the next
level, adding uniqueness and creativity to a variety of projects.
If you are looking to explore the benefits of die cutting
services, get in touch with Color Vision at 800-543-6299. Or, if you already
know your project's specs and would like to receive an emailed quote, simply
click here to submit a quote request. As always, we look forward to discussing your
project and hope to hear from you soon!
Related Articles

Printing Terminology: What are Crop Marks?
Read This Article

Printing Terminology: What is a Printer’s House Sheet?
Read This Article

Printing Ink: What does “Heavy Coverage” mean?
Read This Article

Matte vs Uncoated: Which Paper is better for your Project?
Read This Article